UNDERSTANDING VISION AND ITS ANOMALIES
The human eye works like a camera by capturing images of objects. These images are formed on the retina. The lens accommodates itself depending on the distance, with the aim of reproducing a clear image.
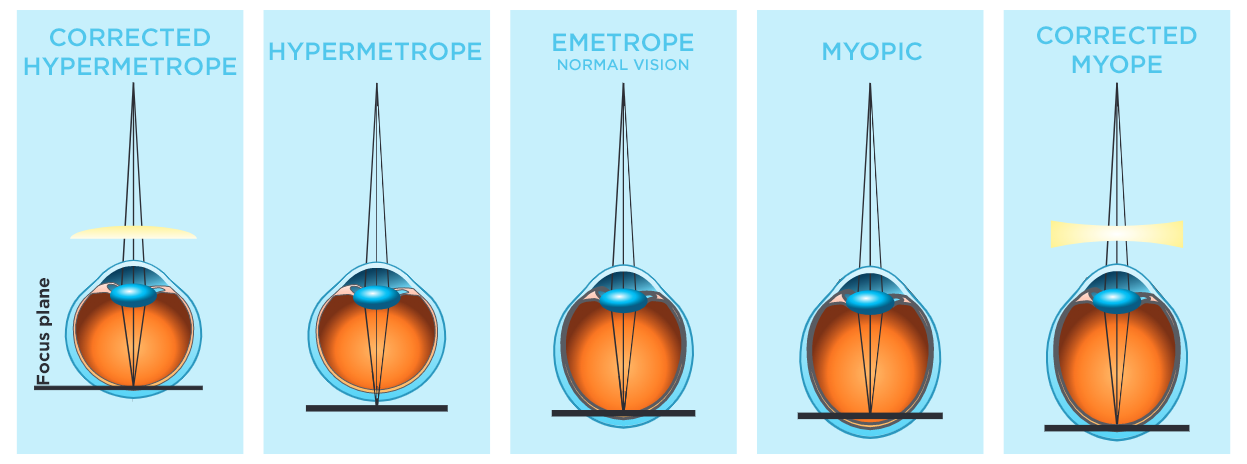
In cases where the image is not correctly formed on the retina, it appears blurred. Which means that there is a deviation in the placement of the image at the anteroposterior level of the eye globe. This effect is called Ametropia and there are three different types to be considered: Myopia, Hypermetropia and Astigmatism, requiring lenses or surgery to correct them.
MYOPIA – DO YOU HAVE DIFFICULTY SEEING FROM A DISTANCE?
Myopia is caused by the eye being too long. In myopia, the distance between the cornea and the retina is greater than normal. In this case, the image of an object is focused in front of the retina, which means that for near-sighted people, near objects appear clear, but objects farther away look blurry. The near-sighted person will have to bring the object close to the eyes to be able to identify it clearly.
Main symptoms
Poor vision from a distance, floaters, eyestrain, and frequent squinting.
How is it corrected?
Myopia is corrected with diverging lenses, commonly known as negative lenses, which allow the image to form on the retina.
HYPERMETROPIA – DO YOU HAVE DIFFICULTY IN SEEING UP CLOSE?
Hypermetropia is caused by anteroposterior shortening of the eye globe, that is, the eye is shorter than normal. The image is focused behind the retina. “They stretch their arm to read,” so that the image is formed on the retina. The far-sighted person generally has good vision from a distance, but nearby objects look blurry.
Main symptoms
Eyestrain, headaches, vague periocular pain, and inflammation of the eyes.
How is it corrected?
Hypermetropia is corrected with converging lenses, also known as positive lenses, which allow images to form clearly on the retina.
ASTIGMATISM – DO YOU HAVE BLURRY SIGHT OR FEEL HEADACHES?
Astigmatism is a visual anomaly caused by the irregular shape of the cornea or crystalline. There are different refractions depending on the horizontal and vertical meridians. There are two focal points which are located on different axes.
A normal cornea is round and smooth. In cases of astigmatism, the cornea is slightly oval in shape rather than spherical. Typically, astigmats have blurred vision, both near and afar.
Main symptoms
Blurred vision, vision stretching.
How is it corrected?
Astigmatism can be corrected with toric or cylindrical lenses that offset corneal irregularities
PRESBYOPIA – RELATED WITH AGEING
Presbyopia is a natural phenomenon related with ageing that normally occurs after the age of forty, and is related to the loss of elasticity of the crystalline, crystalline sclerosis, increased crystalline volume, hypo-accommodation or even loss of elasticity of the ciliary body.
Main symptoms
Similar to those of hypermetropia (need to stretch the arm to read and, after reading, headaches, red eyes, tearing).
How is it corrected?
Presbyopia can be corrected with various types of lenses. The ideal solution is a progressive or bifocal lens, since this type of lens has different focal points depending on the distance to the object
STRABISMUS
Strabismus is caused by the misalignment of the eye muscles. This visual disorder is usually hereditary. The brain controls the eye muscles and when it is affected (tumours, hydrocephalus, paralysis) it can cause strabismus. When the eyes become dull due to cataracts or other injuries, they often become cross-eyed as well.
Main symptoms
Inability to direct the optical axes of the eyes towards the same point.
How is it corrected?
In some cases, this problem can be solved only with the use of prismatic lenses, but, in most cases, the treatment is surgical













